Enhancing LiDAR point cloud generation with BRDF-based appearance modelling
Published in ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2025
Abstract
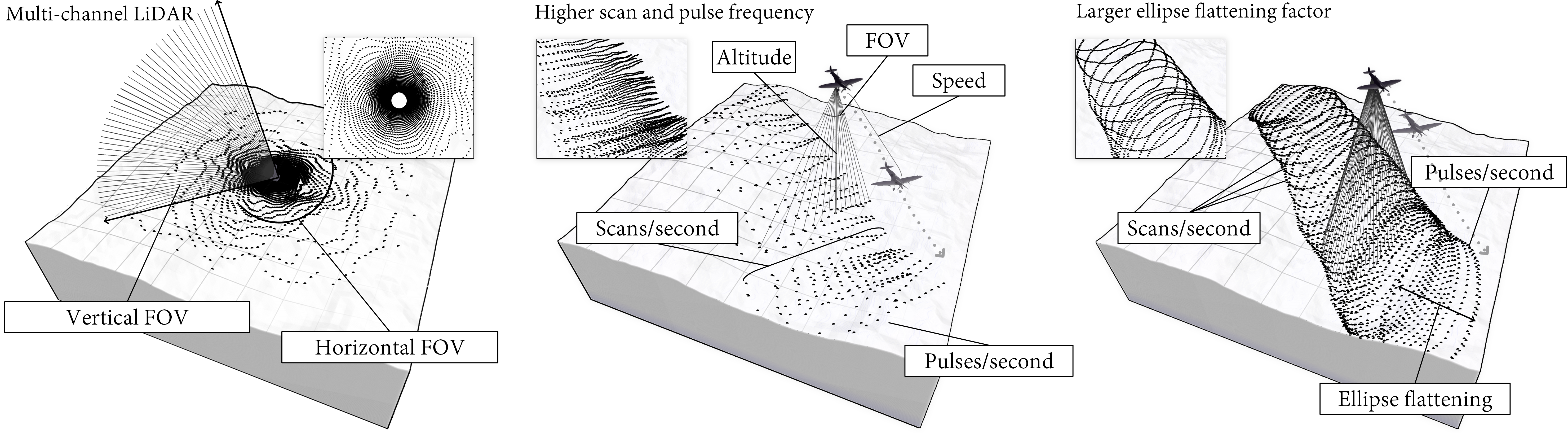
This work presents an approach to generating LiDAR point clouds with empirical intensity data on a massively parallel scale. Our primary aim is to complement existing real-world LiDAR datasets by simulating a wide spectrum of attributes, ensuring our generated data can be directly compared to real point clouds. However, our emphasis lies in intensity data, which conventionally has been generated using non-photorealistic shading functions. In contrast, we represent surfaces with Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Functions (BRDF) obtained through goniophotometer measurements. We also incorporate refractivity indices derived from prior research. Beyond this, we simulate other attributes commonly found in LiDAR datasets, including RGB values, normal vectors, GPS timestamps, semantic labels, instance IDs, and return data. Our simulations extend beyond terrestrial scenarios; we encompass mobile and aerial scans as well. Our results demonstrate the efficiency of our solution compared to other state-of-the-art simulators, achieving an average decrease in simulation time of 85.62\%. Notably, our approach introduces greater variability in the generated intensity data, accounting for material properties and variations caused by the incident and viewing vectors. The source code is available on GitHub (https://github.com/AlfonsoLRz/LiDAR_BRDF).
Recommended citation: López, A., Ogayar, C. J., Segura, R. J., & Casas-Rosa, J. C. (2025). Enhancing LiDAR point cloud generation with BRDF-based appearance modelling. ISPRS Journal Of Photogrammetry And Remote Sensing, 222, 79-98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2025.02.010
Download Paper | Download Bibtex